Part B sẽ ôn lại 9 dạng bài tập quan trọng môn Financial Reporting (F7) với chủ đề Preparation of financial statements.
I. Tổng quan
|
Chủ đề |
Dạng bài |
Câu hỏi tương ứng |
|
|
Trắc nghiệm |
Tự luận |
||
|
1. Consolidated statements of financial positions |
Calculate each element that related to consolidated statements of financial positions |
Câu 4, 5 |
Câu 1 - 3 |
|
2. Consolidated statements of profit or loss and other comprehensive |
1. Profit attributable to NCI & Parent |
Câu 2 |
Câu 1 |
|
2. Profit of Group |
Câu 3 |
||
|
3. Selling Subsidiaries |
Câu 4,5 |
||
|
3. Accounting for associates |
1. Identify an associate |
Câu 1 |
|
|
2. Profit from associate in the consolidated statement |
Câu 2,3 |
||
|
4. Presentation of financial statement |
Presentation of financial statement |
Câu 1 - 3 |
|
|
5. Statement of cash flow |
1. Direct & Indirect statements of cash flow |
Câu 1 |
|
|
2. Activities include in indirect method |
Câu 2 - 5 |
||
II. Dạng bài tập chi tiết
1. Consolidated statements of financial positions
Mức Độ: Quan trọng
1.1. DẠNG 1: Calculate each element that related to consolidated statements of financial positions
Câu 1: Calculate consideration transferred and unrealized profit
Learning outcome: Nắm được công thức tính Calculate consideration transferred và unrealised profit.
Question:
On 1 April 20X7 Root Co acquired 116 million of Branch Co's 145 million ordinary shares for an immediate cash payment of $210 million and issued at par one 10% $100 loan note for every 200 shares acquired.
At the date of acquisition Branch Co owned a recently built property that was carried at its depreciated construction cost of $62 million. The fair value of this property at the date of acquisition was $82 million and it had an estimated remaining useful life of 20 years.
Branch Co also had an internally developed brand which was valued at the acquisition date at $25 million with a remaining life of 10 years.
The inventory of Branch Co at 31 March 20X9 includes goods supplied by Root Co for a sale price of $56 million. Root adds a mark-up of 40% on the cost to all sales.
- What is the total amount of the consideration transferred by Root Co to acquire the investment in Branch Co?
- What is the amount of unrealised profit arising from intragroup trading?
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
CT = cash paid immediately + deferred payment/discount + share exchange
Root Co acquired 116 million of Branch Co's 145 million ordinary shares 🡪 inventory of Branch Co at 31 March 20X9 includes goods supplied by Root Co is intragroup sales 🡪 Unrealised profit = Gross profit from inventory
Answer:
1. Cash paid immediately = $210mShare exchange = 116m*$100/200 = $58m
🡪 CT = $210m + $58m = $268m
2. Unrealised profit = $56m*40/140 = $16mCâu 2: Calculate Non-controlling interest (NCI)
Learning outcome: Nắm được công thức tính NCI
Question:
Witch Co acquired 70% of the 200,000 equity shares of Wizard, its only subsidiary, on 1 April 20X8 when the retained earnings of Wizard Co were $450,000. The carrying amounts of Wizard Co's net assets at the date of acquisition were equal to their fair values. Witch Co measures non-controlling interest at fair value, based on the share price. The market value of Wizard Co shares at the date of acquisition was $1.75. On 31 March 20X9, the retained earnings of Wizard Co were $750,000. At what amount should the non-controlling interest appear in the consolidated statement of financial position of Witch Co on 31 March 20X9?
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
NCI at reporting date = NCI at acquisition date + post-acquisition RE of subsidiaries allocated for non-controlling investor
There are 2 methods for calculating NCI at the acquisition date
- Method 1 partial fair value: NCI = % NCI own * fair value of net assets
- Method 2 full fair value: NCI = number of share NCI own * share price of the subsidiary at the acquisition date
Answer:
Fair value at acquisition = 200,000*$1.75*30% =$105,000
Share of post-acquisition retained earnings = ($750,000 - $450,000)*30% = 90,000$
🡪 NCI = $195,000
Câu 3: Calculate goodwill
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách tính consideration transfer của goodwill
Question:
Johanna acquired 100% of Sidney on 1 January 20X4, paying $5 million cash, including $200,000 professional fees. Johanna also agreed to pay $10 million on 1 January 20X6. Johanna Co has a cost of capital of 10%. Identify the components to be included within the calculation of goodwill for the acquisition of Sidney Co for the year ended 31 December 20X4
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
There are two cases when parent company acquired subsidiaries
- Transfer cash immediately at the acquisition date
🡪 Cash consideration = Amount of cash at acquisition date - Professional fees (if exist)
- Transfer cash in future
🡪 Cash consideration = Amount of cash at transfer day/ (1+ cost of capital)t
With t is a period of time from acquisition day to transfer day
Answer:
- Transfer cash immediately at the acquisition date
Cash consideration = $5,000,000 - $200,000 = $4,800,000
- Transfer cash in future
Cash consideration = $10,000,000/(1+0.1)2 = $8.3m
Câu 4: Calculate goodwill
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách tính consideration transfer của goodwill
Question:
Crash Co acquired 70% of Bang Co's 100,000 $1 ordinary shares for $800,000 when the retained earnings of Bang Co were $570,000. Bang Co also has an internally developed customer list which has been independently valued at $90,000. The non-controlling interest in Bang Co was judged to have a fair value of $220,000 at the date of acquisition. What was the goodwill arising on acquisition?
A. $130,000B. $450,000
C. $380,000
D. $350,000
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
Step 1: Calculate fair value of net assets of subsidiary = Share + RE
Step 2: Calculate Goodwill
Goodwill = Consideration transferred + NCI - fair value of net assets of the subsidiary
Answer: D. $350,000
Consideration transferred = Acquisition price = $800,000
NCI = $220,000
Fair value of net assets of subsidiary = $100,000 + $570,000 = $670,000
🡪 Goodwill = $800,000 + $220,000 - $670,000 = $350,000
Câu 5: Intra-group profits
Learning outcome: Nắm được lý thuyết cơ bản về intra-group profits
Question:
Under certain circumstances, profits made on transactions between members of a group need to be eliminated from the consolidated financial statements under IFRS.
Which of the following statements about intra-group profits in consolidated financial statements is/are correct?
(i) The profit made by a parent on the sale of goods to a subsidiary is only realized when the subsidiary sells the goods to a third party
(ii) Eliminating intra-group unrealized profit never affects non-controlling interests
(iii) The profit element of goods supplied by the parent to an associate and held in year-end inventory must be eliminated in full
A. (i) onlyB. (i) and (ii)
C. (ii) and (iii)
D. (iii) only
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
- Eliminating intra-group unrealized profit never affects non-controlling interests 🡪 False
Unrealized profit will affect non-controlling interests in case subsidiary takes to profit from the parent (subsidiary sells goods for parent)
- The profit element of goods supplied by the parent to an associate and held in year-end inventory must be eliminated in full 🡪 False
Unrealised profit = Total profit from sale * unsold * % owned in associate 🡪 Just be partly eliminated
Answer: A. (i) only
2. Consolidated statements of profit or loss and other comprehensive
Mức Độ: Quan trọng
2.1. DẠNG 1: Profit attributable to NCI & Parent
Câu 1: Attributable to NCI
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách tính lợi nhuận phân bổ cho cổ đông không kiểm soát
Question:
Brigham Co has owned 70% of Dorset Co for many years. It also holds a $5 million 8% loan note from Dorset Co. One of Dorset Co's non-current assets has suffered an impairment of $50,000 during the year. There is a balance in the revaluation surplus of Dorset Co of $30,000 in respect of this asset. The impairment loss has not yet been recorded. The entity financial statements of Dorset Co show a profit for the year of $1.3 million.
What is the amount attributable to the non-controlling interests in the consolidated statement of profit or loss?
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
Profit attributable for NCI = (Profit for subsidiary - amendment items)*%own of NCI
Step 1: Calculate profit for subsidiary
Step 2: Calculate amendment items = unrealized profit + Impairment - revaluation surplus
Answer:
Profit for subsidiary = $1.3 million.
Unrealized profit = $5m *8% = $400,000.
Impairment - revaluation surplus = $50,000 - $30,000 = $20,000.
%own of NCI = 100% - 70% =30%
🡪 Profit attributable for NCI = $264,000
Câu 2: Attributable to Parent
Learning outcome:
Question:
On 1 January 20X5, Prunier acquired 80% of Sheringham’s two million $1 ordinary shares. At this date, Sheringham had retained earnings of $4 million and a revaluation surplus of $2 million. Prunier had retained earnings of $10 million and a revaluation surplus of $5 million. The fair value of Sheringham’s net assets at acquisition were equal to their carrying amounts with the exception of Sheringham’s property which had a fair value of $800,000 in excess of its carrying amount and remaining life of 20 years.
On 31 December 20X5, Prunier and Sheringham both revalued their assets. Prunier’s assets increased by a further $2 million while Sheringham’s increased by $500,000. At this date, Prunier’s retained earnings were $11 million and Sheringham’s were $3.5 million $40,000.
What will be the other comprehensive income attributable to the parent for the year ended 31 December 20X5
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
The other comprehensive income attributable to the parent will be 100% of the parent‘s revaluation gain in the year and its %own at subsidiary post-acquisition revaluation gain.
Answer: $2,400,000
The other comprehensive income attributable to the parent = $2m + 80%*$0.5m = $2.4m
2.2. DẠNG 2: Profit of Group
Câu 3: Intra-group selling
Learning outcome:
Question:
Basil Co acquired 60% of Parsley Co on 1 March 20X9. In September 20X9 Basil Co sold $46,000 worth of goods to Parsley Co. Basil Co applies a 30% mark-up to all its sales. 25% of these goods were still held in inventory by Parsley Co at the end of the year. An extract from the draft statements of profit or loss of Basil Co and Parsley Co at 31 December 20X9 is:
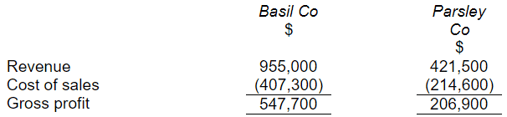
All revenue and costs arise evenly throughout the year.
What will be shown as gross profit in the consolidated statement of profit or loss of Basil Co for the year ended 31 December 20X9?
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
Gross profit Group = Gross profit P + Gross Profit S – URP
Step 1: Identify Gross profit P
Step 2: Gross Profit S = Year-end gross profit*time apportioned
Step 3: Calculate unrealized profit (from intragroup sale)
Answer:
Gross profit P = $547,700
Gross Profit S = $206,900*10/12 (from 1/3/20X9-31/12/20X9) =$172,417
Unrealized profit = (46,000 × 30 / 130) × 25% = 2,654
🡪 Gross profit Group = 717,463
2.3. DẠNG 3: Selling Subsidiaries
Câu 4: Profit from disposal of subsidiary
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách xác định lợi nhuận thu được từ việc bán công ty con trên báo cáo kết quả kinh doanh hợp nhất.
Question:
On 30 June 20X4, the Tea group disposed of its 60% holding in the ordinary shares of Coffee for $15 million in cash. The non-controlling interest at the acquisition date was measured at its fair value of $2.2 million. Coffee’s net assets at the acquisition and the disposal date were $5 million and $8 million respectively. Goodwill arising on the acquisition of Coffee of $1 million had been fully impaired by the disposal date.
What is the profit arising from the disposal of Coffee that will be recorded in the consolidated statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31 December 20X4?
A. Profit of $10.0 millionB. Profit of $9.2 million
C. Profit of $10.4 million
D. Profit of $10.2 million
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
Step 1: Calculate Non-Controlling Interest at the disposal
Non-Controlling Interest at disposal = Non-controlling interest at acquisition + %NCI of post-acquisition net assets - %NCI of goodwill impairment
Step 2: Profit = Sale proceeds + Non-Controlling Interest at disposal - Net asset of the subsidiary at disposal - Goodwill at disposal
Answer: A. Profit of $10.0 million
Non-controlling interest at acquisition = $2.2m
%NCI of post-acquisition net assets = 40% * ($8m- $5m) = $1.2m
%NCI of goodwill impairment = 40% * 1m = $0.4m
🡪 Non-Controlling Interest at disposal = $2.2m + $1.2m - $0.4m = $3m
Net asset of the subsidiary at disposal = $8m
Goodwill at disposal = 0
Sale proceeds = $15m
🡪 Profit arising on the disposal = $15m + $3m - $8m = $10m
Câu 5: Recognise profit prom disposal of subsidiary in Parent’s FS
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách xác định lợi nhuận thu được từ việc bán công ty con trên báo cáo kết quả kinh doanh hợp nhất.
Question:
Alderminster Co acquired a 70% holding in Bidford Co on 1 January 20X4 for $600,000. At that date, the fair value of the net assets of Bidford Co was $700,000. Alderminster Co measures non-controlling interest at its share of net assets. On 31 December 20X6 Alderminster Co sold all its shares in Bidford Co for $950,000. At that date, the fair value of Bidford Co's net assets was $850,000. Goodwill was not impaired. What was the profit or loss on disposal to be recognised in the consolidated financial statements of Alderminster Co?
A. $135,000B. $200,000
C. $245,000
D. $355,000
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy):
Step 1: Calculate Non-Controlling Interest at disposal
Non-Controlling Interest at disposal = Non-controlling interest at acquisition + %NCI of post-acquisition net assets - %NCI of goodwill impairment
Step 2: Profit = Sale proceeds + Non-Controlling Interest at disposal - Net asset of subsidiary at disposal - Goodwill at disposal
Answer: C. $245,000
Non-Controlling Interest at disposal = 30%*$850,000 = $255,000m
Net asset of subsidiary at disposal = $850,000
Goodwill at disposal = $600,000 - 70%*$700,000 = $110,000
Sale proceeds = $950,000
🡪 Profit arising on the disposal = $950,000 - $850,000 - $110,000 + $255,000= $245,000
3. Accounting for associates
Mức Độ: Quan trọng
3.1. DẠNG 1: Identify an associate
Câu 1:
Learning outcome:
Question:
Which of the following would be classified as an associate?
A. Own 80% of the preference sharesB. Own 55% of the ordinary shares
C. Own 15% of the ordinary shares and engage in building operating policy and company finance
D. Own 50% of the ordinary shares and manipulate operating policy and company finance
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
Feature of associate
- Own about 20%-50% of company
- Have significant influence in company, but not control company
Answer: C. Own 15% of the ordinary shares and engage in building operating policy and company finance
Own 80% of the preference shares - well a preference share is pretty much like giving a loan - you don't have any voting rights - so there's no significant influence there
Own 55% of the ordinary shares - well these do have voting rights - so here you effectively control the entity - not just a significant influence
Own 50% of the ordinary shares and manipulate operating policy and company finance 🡪 control the entity
Own 15% of the ordinary shares and engage in building operating policy and company finance - 🡪 have a significant influence
3.2. DẠNG 2: Profit from associate in the consolidated statement
Câu 2: Share of profit from assiociate in P/L
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách xác định lợi nhuận từ công ty liên kết ghi nhận trong báo cáo lãi lỗ hợp nhất
Question:
Burridge bought 30% of Allen on 1 July 20X4. Allen’s statement of profit or loss for the year shows a profit of $400,000. Allen paid a dividend to Burridge of $50,000 on 1 December 20X4. At the year end, the investment in Allen was judged to have been impaired by $10,000.
What will be the share of profit from associate shown in the consolidated statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31 December 20X4?
A. $57,000B. $50,000
C. $60,000
D. $110,000
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
Share of profit of associate = %own in associate of group * profit after tax of associate* time apportioned – impairment loss
Answer: C. $50,000
% own in the associate of group = 30%
Profit after tax of associate = $400,000
Time apportioned = 6/12 (1 July 20X4 - 31 December 20X4)
Impairment loss = $10,000
🡪 Share of profit of associate = $50,000
The dividend would not have been in Allen’s statement of profit or loss, so no adjustment to this would be made. The adjustment to remove the dividend would be made in investment income, where Burridge will have recorded the income in its individual financial statements
Câu 3: Investment in associates
Learning outcome: Biết được cách tính khoản đầu tư từ công ty liên kết ghi nhận trong BKĐKT của công ty
Question:
On 1 October 20X8 Pacemaker Co acquired 30 million of Vardine Co's 100 million shares in exchange for 75 million of its own shares. The fair value of Pacemaker Co's shares at the date of this share exchange was $1.60 each. Vardine Co's profit is subject to seasonal variation. Its profit for the year ended 31 March 20X9 was $100 million. $20 million of this profit was made from 1 April 20X8 to 30 September 20X8. Pacemaker Co has one subsidiary and no other investments apart from Vardine Co.
What amount will be shown as 'investment in associate' in the consolidated statement of financial position of Pacemaker Co as of 31 March 20X9?
A. $144 millionB. $150 million
C. $78 million
D. $126 million
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
Step 1: Calculate investment in Associate at the acquisition date
Step 2: Net asset post-acquisition earnings = Net asset at the end - Net asset at the acquisition date
Step 3: Calculate % own in the associate of group = Own share/Total share of associate
Step 4: Investment in Associate at the end of period = Investment in Associate at acquisition date + net asset post-acquisition earnings * % own in the associate of the group
Answer: $144 million
Investment in Associate at acquisition date = 75m *$1.6 = $120m.
Net asset post-acquisition earnings = Share of post-acquisition retained earnings
= $100m- $20m = $80m.
% own in associate of group = 30m/100m = 30%.
🡪 Investment in Associate at the end of period = $120m + 30%*$80m = $144m.
4. Presentation of financial statement
Mức Độ: Ít quan trọng
Câu 1: Classified current liability
Learning outcome:
Question:
Which one of the following would NOT necessary lead to a liability being classified as a current liability?
A. The liability is expected to be settled in the course of the entity's normal operating cycleB. The liability has arisen during the current accounting period
C. The liability is held primarily for the purpose of trading
D. The liability is due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the reporting period
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
There are 3 principles
- The liability is expected to be settled in the course of the entity's normal operating cycle
- The liability is held primarily for the purpose of trading
- The liability is due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the reporting period
Answer: B. The liability has arisen during the current accounting period
Câu 2: Understanding of Presentation of published financial statements
Learning outcome: Nắm được kiến thức cơ bản về Presentation of published financial statements
Question:
Which of the following does not comprise a set of financial statements?
A. Statement of financial position as at the end of the periodB. Statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income, changes in equity and cash flow for the period
C. Report of the entity’s sources of funding
D. Comparative information in respect of the preceding period and notes, comprising significant accounting policies and other explanatory information
Answer: C. Report of the entity’s sources of funding – IAS 1- point 10
Câu 3: Statements of changes equity
Learning outcome: Nắm được kiến thức cơ bản về Presentation of published financial statements
Question:
Which of the following could NOT appear as separate items in the statement of changes in equity required by IAS I Presentation of Financial Statements as part of a company’s financial statements?
A. Gain on revaluation of land.B. Loss on sale of investments.
C. Prior year adjustments.
D. Proceeds of an issue of ordinary shares.
Answer: B. Loss on sale of investments.
The loss on sale of investments will be recognised in the statement of comprehensive income.
5. Statement of cash flow
Ref: Tóm tắt kiến thức Topic 5: Statement of cash flow
Mức Độ: Quan trọng
5.1. DẠNG 1: Direct & Indirect statements of cash flow
Câu 1: Direct statements of cash flow
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách yếu tố có trong một báo cáo lưu chuyển tiền tệ theo 2 phương pháp trực tiếp và gián tiếp
Question:
Which item would be NOT be shown in a statement of cash flow using the direct method?
A. Cash payments to employeesB. Cash paid to suppliers
C. Cash sales
D. Finance costs
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
- Direct method: disclose major classes of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments
- Indirect method: net profit or loss is adjusted for the effects of transactions of a non-cash nature, any deferrals or accruals of past or future operating cash receipts or payments, and items of income or expense associated with investing or financing cash flows
Answer: D. Finance costs
5.2. DẠNG 2: Activities include in indirect method
Câu 2: Identify items include in operating activities
Learning outcome: Phân biệt được 3 loại hoạt động operating, investing và financing
Question:
IAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows sets out the three main headings to be used in a statement of cash flows. Which TWO of the items below would be included under the heading 'Cash flows from operating activities' according to IAS 7?
A. Tax paidB. Purchase of investments
C. Loss on disposal of machinery
D. Purchase of equipment
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
- Operating activities are the principal revenue-producing activities of the entity and other activities that are not investing or financing activities.
- Investing activities are the acquisition and disposal of non-current assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents.
- Financing activities are activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the equity capital and borrowings of the entity
Answer: A-C
Purchase of investments 🡪 Investing activities
Purchase of equipment 🡪 Investing activities
Câu 3: The calculation of net cash from operating activities
Learning outcome: Nắm được cơ chế điều chỉnh khi tính toán các chỉ tiêu trong báo cáo lưu chuyển tiền tệ
Question:
Identify the correct treatment in the calculation of net cash from operating activities
under the indirect method.
|
Add to profit before tax |
Deduct from profit before tax |
|
|
Decrease in trade receivables |
||
|
Increase in inventories |
||
|
Profit on sale of non-current assets |
||
|
Depreciation |
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
Step 1: Identify whether the items include in what type of cash flow: Non-cash income/expense
Non-cash expense 🡪 add to profit before tax
Non-cash income 🡪 deduct from profit before tax
Step 2: To assess other items we rely on following table
|
Add to profit before tax |
Deduct from profit before tax |
|
Decrease in inventories/trade and other receivables/prepayments |
Increase in inventories/trade and other receivables/prepayments |
|
Increase in trade and other payables/ accruals/provisions |
Decrease in trade and other payables/ accruals/provisions |
Answer:
|
Add to profit before tax |
Deduct from profit before tax |
|
|
Decrease in trade receivables |
X |
|
|
Increase in inventories |
X |
|
|
Profit on sale of non-current assets |
X |
|
|
Depreciation |
X |
Câu 4: Investing activities
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách tính toán cash flow từ hoạt động investing
Question:
The statement of financial position of Pinto Co at 31 March 20X7 showed property, plant and equipment with a carrying amount of $1,860,000. At 31 March 20X8 it had increased to $2,880,000. During the year to 31 March, 20X8 plant with a carrying amount of $240,000 was sold at a loss of $90,000; depreciation of $280,000 was charged and $100,000 was added to the revaluation surplus in respect of property, plant, and equipment.
What amount should appear under 'investing activities' in the statement of cash flows of Pinto Co for the year ended 31 March 20X8 as cash paid to acquire property, plant, and equipment?
A. $1,640,000B. $1,440,000
C. $1,260,000
D. $1,350,000
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
Step 1: Identify outflow cash and inflow cash
Outflow cash = Cash payments for acquiring PPE (purchase)
Inflow cash = Cash receipts from sales of PPE (disposal)
Step 2: Cash receipts from sales of PPE
Step 3: Calculate outflow cash
Closing PPE = Opening PPE + revaluation + purchase + provision - disposal - depreciation
🡪 Cash payments for acquiring PPE
= (Closing PPE - Opening PPE) + (disposal + depreciation) - (revaluation + provision)
Answer: B. $1,440,000
Cash receipts from sales of PPE = Carrying amount + Depreciation - revaluation surplus =
Cash payments for acquiring PPE
= ($2,880,000m - $1,860,000m) + ($240,000+$280,000) - $100,000
= $1,440,000
Note that: Loss on sale of PPE 🡪 Non-cash expense 🡪 Not include in Investing operating
Câu 5: Share in investing activities
Learning outcome: Nắm được cách tính toán cash flow từ hoạt động investing
Question:
Butcher had the following balances in its statement of financial position as at
30 June 20X0 and 20X1:
|
20X1 |
20X2 |
|
|
Share capital |
$170,000 |
$150,000 |
|
Share premium |
$105,000 |
$95,000 |
|
10% debentures |
$170,000 |
$190,000 |
How much will appear in the statement of cash flows for the year ended 30 June 20X1
under the heading ‘cash flows from financing activities’?
Guidance (Tips/ Steps/ Cách tư duy)
Step 1: Calculate inflow and outflow cash
Share capital and share premium is equity 🡪 Value of them decrease 🡪 Paid less cash for shareholder 🡪 Inflow cash
Debentures are a liability 🡪 Value of debentures increase 🡪 Outflow of cash
Step 2: Cash flow from financing activities = Cash inflow – Cash outflow
Answer: $10,000 inflow (30,000 inflow from share capital and share premium; 20,000 outflow cash from debentures)
-1.png?height=120&name=SAPP%20logo%20m%E1%BB%9Bi-01%20(1)-1.png)